With so many formal governmental organizations and international groups that have been formed, it’s easy to become confused about the various organizations and their roles. For example, many are unaware of the G20 and its primary role. If you’re interested in learning more, continue reading. Below is some information about the G20, its members, its agenda, and its global mission.
What is the G20 and why was it Formed?
The G20, short for the Group of Twenty, was founded in 1999 with the primary purpose to discuss international financial stability. Also referred to as G-20, this organization is an international forum for heads of governments, states and heads of central banks. It is a place for them to discuss and promote international trade, global economic growth, as well as regulations concerning financial markets. The G20 is also comprised of heads of finance ministers and foreign ministers. Collectively the members are from 19 different countries and the European Union (EU). The G20 often holds annual inaugural leaders’ summit.
The G-20 is a forum and is not a legislative body. Therefore, their decisions, agreements and other resolves do not necessarily have a legal impact. However, they do have the ability to influence and shape their country’s financial policies and the overall global cooperation among heads of governments, states, and ministers of finance.
Leaders of the G20 had summits twice in 2009 and 2010. In November of 2011, they held the Cannes Summit and have been holding the summit annually since that time.
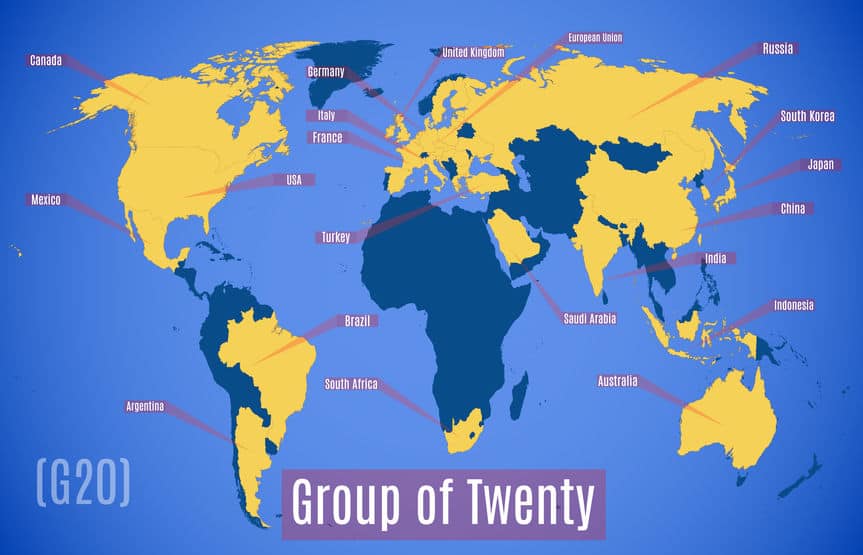
Who are the Members of the G20?
The 19 different countries and the EU that make up the G20 include both major developed countries and developing countries. The members consist of the following:
• Argentina
• Australia
• Brazil
• Canada
• China
• France
• Germany
• India
• Indonesia
• Italy
• Japan
• Republic of Korea
• Mexico
• Russia
• Saudi Arabia
• South Africa
• Turkey
• United Kingdom
• The United States, and the
• European Union
The G20 members are comprised of a mixture of the world’s most advanced countries, as well as some of the emerging countries. The EU represents the European Commission and the European Central Bank. Collectively G20 represents roughly two-thirds of the world’s total population. They also represent 85 percent of the total global gross domestic product and more than 75 percent of the global trade.
Having a membership in the G20 ensures that key countries are exposed to policies and affairs that have a favorable impact on the global economy as a whole. However, the group is also concerned about its impact on non-member countries. As a result, they allow guest countries to attend and participate in their events. They also allow other non-member countries to contribute to their agenda so that their affairs and decisions represent a broader range of international opinions and concerns.
The G7 and Its Ties to the G20
Similar to the G20, the G7 is a smaller group of seven of the world’s largest developed countries. They consist of
• France
• Germany
• Italy
• Japan
• The United States
• The United Kingdom, and
• Canada
The G7 was established in 1975 to basically address international issues associated with finance and economics. They meet each year at their annual summit but allow a wider group of international leaders to attend.
In addition to ministers of finance, their members also include chief ministers, such as presidents and prime ministers. They’ve been referred to as more of a political body since they embrace presidents, chief ministers, prime ministers, and other political leaders.
Members of the G7 are tied to the G20 because they are also members of the G20. As indicated above, members of the G7 are exclusively comprised of well-established, developed countries. The remaining 12 countries are what make up the G20. They consist of the developing countries.
The purpose of establishing the G20 was to create a forum whereby both the developed and developing countries can participate.

Objective and Primary Policies
During the initial G20 summits, it was mainly attended by central bank governors and ministers of finance. However, after the global financial crisis took place in 2008, that changed. The group changed its focus to more of an emergency council that also included prime ministers and presidents. This change was made to address the global financial crisis that resulted in banks collapsing, increases in unemployment rates and stagnated wages.
When the world leaders come together, they discuss the most urgent issues that they are presented with. Particularly those that are related to economic and finance along with its global impact.
Some of the issues addressed consists of climate changes, migration and refugees, trade mispricing, international trade and the world economy in general. However, other issues are addressed in a separate one-on-one basis or in smaller groups. These include issues such as tariffs, various spending measures, taxes on imports and exports, the management of cease-fires and other war-related issues. These discussions often result in debates. The intent is to come to whatever agreement is necessary to move issues forward.
During summits that only have a small number of leaders in attendance, discussions and decisions can be made a lot faster.
According to the BBC, the summits have also been referred to but dismissed as the “talking shop”, meaning that very little significant progress is being made. In any case, since there are no formal votes at the meetings, issues that are agreed to are not legally binding.
Certain changes in policies or the lack thereof create civil unrest in various countries. When topics are discussed at the G20 summits surrounding sensitive issues, it sometimes results in demonstrations that take place near the summit. Such as the protest that occurred in London in 2009 where Ian Tomlinson, a newspaper seller, was killed while he was caught up in a protest on his way home.
Other protest took place as well, such as the one in Buenos Aires in 2018 where thousands of demonstrators marched to protest against the economic policies that were addressed by the G20 world leaders.
Current Agenda Items
According to the Council on Foreign Relations, the 2019 G20 summit, will take place in Osaka, Japan. The agenda will consist of a discussion about global health, a reform of the World Trade Organization (WTO), and climate change. Any bilateral meetings that take place on the summit’s sidelines, will likely lead to major international agreements between leaders.
Support From Non-Member, International Government-Based Organizations
To assist them in their efforts, the mission and work performed by the G20 have been supported by several other international organizations. These organizations provide invaluable policy advice and significantly contribute to the success of the G20.
The international organizations provide useful advice on the G20’s priorities. They accomplish this by assisting them with identifying gaps in policies whereby certain actions can have a significantly larger impact on their efforts.
Key representatives of various international organizations are invited to certain G20 meetings where their advice is most useful. These meetings include:
• Meetings of Sherpas
• Finance Deputies, and
• Working Groups
The international organizations consist of the following:
• The Financial Stability Board (FSB). The FSB was developed by the G20 leaders after the initial global financial crisis took place. They are responsible for coordinating the work associated with the international standard-setting bodies and the national financial authorities. The purpose is to both develop and promote financial related policies, impactful regulations, supervisory roles, and other financial related matters.
• The International Labor Organization (ILO). The ILO is responsible for promoting the rights that should take place in the workplace. They are also responsible for encouraging adequate employment opportunities while increasing social protection. Additionally, they are responsible for strengthening the dialogue surrounding work-related issues.
• The International Monetary Fund (IMF). The IMF is responsible for securing financial stability while fostering global monetary cooperation among nations. Their role also consists of facilitating international trade, promoting higher employment rates and sustaining economic growth. The IMF also develops ways to reduce world poverty.
• The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Since the OECD promotes policies known to improve both the economic and social well-being of individuals on a worldwide basis, their role is to work directly with governments to assist them better understand what drives environmental, social and economic change. They accomplish this by focusing on analyzing and comparing financial data that will help them better predict future trends.
• The United Nations (UN). The UN is committed to global safety and thus promotes and develops policies to better maintain international security and peace. Their work also involves the development of friendly relationships between nations. This role is performed in conjunction with promoting better living standards, enhancing social progress, and improving human rights.
• The World Bank. The World Bank has been known for its commitment to assisting developing nations on a worldwide basis. They are a vital and powerful source for providing technical and financial assistance to the countries across the globe that need it the most. The World Bank is not a typical bank. They offer an exceptionally unique partnership with the intent to assist the G20 with their efforts to reduce poverty while also supporting development efforts.
• The World Trade Organization (WTO). The WTO works with the G20 to provide a forum designed specifically for monitoring and implementing agreements and providing a setting for negotiations. Their goal and responsibilities are to assist in reducing the obstacles associated with international trade. They also have a commitment to ensuring that each nation has a level playing field. The WTO also contributes to the overall economic growth and development of nations with the greatest needs.
Additional Support from Non-Government Organizations
In addition to receiving support from government-based organizations, the G20 can also credit its success to other non-governmental organizations as well. They engage with organizations in various sectors on an on-going basis. These non-government sectors consist of the following:
• The Business Sector – (B20)
• Civil Society – (C20)
• Labor – (L20)
• Think Tanks – (T20)
• Youth – (Y20)
Together these groups hold major events throughout the year whereby their outcomes contribute to the efforts and deliberations of the global G20 leaders.
The Bottom Line
The summit lends itself to the development of both professional and personal relationships across multiple international borders that may not have been formed otherwise. These relationships have a significant impact on agreements that are made and the development of foreign policies. To that end, experts emphasize the substantial impact that personal relationship between global leaders has on policies. When these policies are put in place, they can last for decades according to experts. By the G20 summit bringing so many national leaders together, it provides the rare opportunity for them to form relationships that build and strengthen economic, social and human rights.